What if one small change could make your supply chain more predictable and your fulfillment more reliable?
That is exactly what happens when retailers use the Advanced Shipping Notice (ASN), a document that provides shipment details before the goods arrive.
Instead of guessing what is on the way, retailers know which products are coming, in what quantities, and when to expect them. The result is smoother receiving, faster inventory updates, and fewer fulfillment issues.
The challenge is that many businesses overlook the importance of ASN or struggle to implement it effectively, leaving operations exposed to delays and errors.
This guide explains what ASN is, why it matters, and how to use it correctly in retail logistics.
What Is an Advanced Shipping Notice (ASN)?
An Advanced Shipping Notice (ASN) is an electronic document, often referred to as an EDI 856, that suppliers send to retailers before a shipment arrives. It provides detailed information about the shipment so retailers can prepare their receiving teams, update inventory systems in advance, and streamline supply chain operations.
For major retailers such as Walmart and Amazon, ASN compliance is not optional. It is a core requirement for efficient logistics and accurate fulfillment.
Key Information Provided in an ASN
A well-prepared ASN typically includes:
- Detailed shipment list: Product descriptions, quantities, SKUs, or UPCs.
- Packaging information: Carton numbers, pallet IDs, and packaging hierarchy.
- Estimated arrival: Expected delivery date and time.
- Carrier and tracking information: Details of the transport provider with PRO/BOL numbers or tracking IDs.
- Compliance data: Retailer-specific codes and regulatory data, such as GLNs or expiration dates.
- Pre-receipt inventory data: Information that allows inventory systems to update before goods arrive.
How Does an ASN Work?
An Advanced Shipping Notice (ASN) works by transmitting detailed shipment data electronically, often through EDI 856, from the supplier to the retailer before the goods arrive. This early exchange of information ensures retailers are ready to receive, verify, and process shipments accurately.
Key technologies involved:
-
EDI (Electronic Data Interchange): Standard format for sending ASNs.
-
Supplier ERP/WMS systems: Generate shipment details directly from order and warehouse data.
-
Retailer inventory systems: Receive ASN data to prepare for inbound goods.
-
Barcode and RFID scanning: Match shipment data to physical goods.
-
Integration with carrier systems: Provide tracking and logistics updates.
Steps involved:
-
Order fulfillment begins: The supplier prepares goods for shipment and generates ASN data in their ERP or WMS.
-
ASN transmission: The supplier sends the ASN (EDI 856) electronically to the retailer, including shipment details like SKUs, packaging, carrier info, and estimated arrival.
-
Retailer system update: The retailer’s inventory system uses ASN data to anticipate incoming goods and schedule receiving resources.
-
Shipment in transit: Carriers transport the goods while ASN data allows tracking and visibility.
-
Receiving preparation: Warehouse teams use ASN data to match expected vs. actual deliveries, organize unloading, and speed up check-in.
-
Verification on arrival: Barcodes or RFID tags are scanned to reconcile items against the ASN, ensuring accuracy and identifying discrepancies.
-
Inventory update: Once verified, inventory records are updated in real-time before items move into storage or fulfillment.
-
Exception handling: Any shortages, overages, or damaged items are flagged immediately for resolution.
The Importance of ASN Accuracy and Compliance
Understanding how to start my own shipping company is essential, as these operations play a vital role in maintaining supply chain efficiency and inventory accuracy.
Retailers set stringent standards for ASN submissions, and failure to comply often results in chargebacks, delayed receiving, or operational disruptions.
For Businesses: Efficiency, Accuracy, and Compliance
-
Timely preparation: On-time ASNs allow warehouse teams to plan labor, dock space, and equipment before shipments arrive.
-
Accurate inventory management: Correct ASN data ensures smooth reconciliation between shipments and records, reducing manual interventions.
-
Reduced chargebacks: Accurate and timely ASNs help suppliers avoid costly retailer penalties and deduction claims.
-
Vendor performance protection: Consistently compliant ASNs safeguard a supplier’s scorecard and maintain preferred vendor status.
-
Automated efficiency: Integrating EDI with ERP reduces manual entry errors, speeds up processing, and ensures consistent submissions.
For Retailers: Visibility, Planning, and Reliability
-
Advance shipment visibility: Retailers know exactly what is on the way, in what quantities, and when it will arrive.
-
Optimized receiving: Accurate ASNs streamline scheduling at distribution centers and reduce delays in unloading or sorting.
-
Improved fulfillment performance: Correct data ensures faster inventory updates, leading to better product availability for customers.
-
Fewer disputes: Reliable ASNs reduce mismatches and minimize time spent resolving errors between suppliers and retailers.
Consequences of ASN Errors and Non-compliance
-
Preparation delays: Missing or late ASNs prevent warehouse teams from organizing labor, dock space, and equipment in advance. This leads to slower receiving and processing.
-
Inventory discrepancies: Inaccurate data creates mismatches between shipments and system records, forcing manual intervention and delaying inventory updates.
-
Chargebacks: Retailers often penalize suppliers with financial deductions for incorrect or untimely ASNs, adding direct costs to operations.
-
Vendor scorecard impact: Frequent ASN errors negatively affect vendor performance ratings, which can threaten preferred vendor status or future business opportunities.
Best Practices Checklist for ASN Submission
To meet retailer expectations and avoid financial penalties, suppliers should follow these best practices:
-
Submit on time: Transmit the ASN before the shipment arrives at the retailer’s distribution center.
-
Validate accuracy: Double-check item counts, packaging details, and carrier information against the physical shipment.
-
Follow retailer rules: Ensure the ASN meets the specific formatting, codes, and compliance requirements of each retailer.
-
Automate where possible: Use EDI integrated with ERP or WMS to reduce manual errors and improve speed.
-
Test regularly: Perform routine EDI testing and monitor acknowledgment responses (EDI 997 or 824) to detect and resolve errors quickly.
ASN Process Workflows at Walmart and Amazon
Both Walmart and Amazon have strict ASN protocols designed to ensure shipment accuracy and compliance. While the core purpose is the same, their workflows have distinct requirements.
Walmart ASN workflow:
Walmart’s ASN process revolves around three core EDI transactions:
-
EDI 856 (Advance shipment notice): Suppliers send this file to Walmart containing the shipment hierarchy and product details.
-
EDI 997 (Functional acknowledgment): Upon receiving the EDI 856, Walmart responds with an EDI 997, which either:
-
Confirms successful acceptance of the data.
-
Indicates rejection if there are issues with the document structure or content.
-
-
EDI 824 (application advice): Even after a successful EDI 997, suppliers must monitor for an EDI 824 transmission. This document provides more detailed feedback:
An ASN with "ERROR" or "WARN" text indicates issues such as missing or invalid UPCs (Universal Product Codes) or GLNs (Global Location Numbers).
-
Warn: Indicates minor issues that do not prevent data usage but should be corrected.
-
Error: Indicates critical issues leading to complete rejection. Errors should be corrected and resent before the ASN is considered valid or accepted by the retailer.
-
Walmart has provided over 100 deduction reasons for chargebacks. Check out our detailed guide on Walmart deduction codes.
Recent developments: As of May 2024, Walmart has tightened its ASN standards. The ASN Dashboard in Retail Link now provides enhanced visibility, allowing suppliers to proactively identify and fix recurring ASN submission errors.
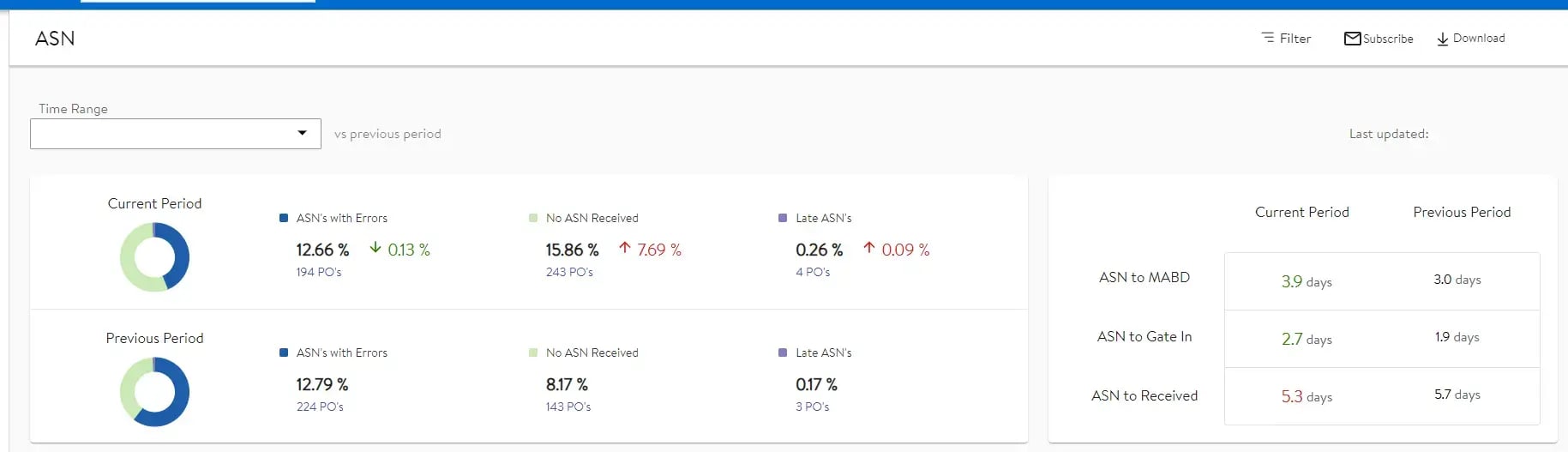
Amazon ASN workflow:
Amazon's ASN expectations are similarly demanding:
-
Timely submission: ASNs must be sent before goods arrive at Amazon’s Fulfillment Center.
-
Unit accuracy: The quantity listed on the ASN must match the physical contents precisely.
-
Valid ARN (Amazon reference number): Amazon requires a valid Amazon Reference Number for all shipments.
-
Correct PRO/BOL details: Prepaid shipments must have the correct Bill of Lading or PRO number.
- Expiration Dates: Perishable or regulated items must include accurate shelf-life data.
Common Amazon ASN failure modes:
- Late ASN submissions or batching delays
-
Incorrect or missing ARN, PRO, or BOL numbers
-
Mismatched quantities between ASN and shipment
-
Receiving errors at Amazon Fulfillment Centers, occasionally leading to invalid deductions
Walmart vs Amazon ASN Requirements
| Aspect | Walmart ASN | Amazon ASN |
|---|---|---|
| Submission Timing | ASN (EDI 856) must be sent before goods arrive at Walmart distribution centers. | ASN must be submitted before goods arrive at Amazon Fulfillment Centers. |
| Key Document | EDI 856 (Advance Shipping Notice) | EDI 856 (Advance Shipping Notice) |
| Acknowledgment | EDI 997 (Functional Acknowledgment) confirms acceptance or rejection. | No formal EDI 997 acknowledgment, but shipment may be flagged for errors if incorrect. |
| Error Feedback | EDI 824 provides warnings (minor issues) or errors (critical, requires resend). | Issues flagged through shipment processing errors or deduction notices. |
| Critical Data Points | Product hierarchy, SKUs/UPCs, GLNs, packaging details, arrival times. | Valid ARN, PRO/BOL numbers, unit accuracy, expiration dates for perishables. |
| Compliance Risks | Over 100 deduction codes tied to ASN errors; stricter standards as of May 2024. | Deductions for late ASNs, quantity mismatches, missing ARN/PRO/BOL, or invalid data. |
| Recent Updates | ASN Dashboard in Retail Link for visibility into recurring submission errors. | No dashboard, but stricter enforcement of ARN and expiration date accuracy. |
Common ASN Challenges for Suppliers
Managing ASNs across multiple retailers is rarely straightforward. Suppliers face a range of recurring challenges that can impact compliance, efficiency, and profitability.
-
Data inaccuracies: Incorrect UPCs, mismatched quantities, invalid location codes, or missing packaging hierarchies often lead to ASN rejections.
-
Late submissions: Human error, ERP delays, or EDI integration issues can cause ASNs to be transmitted after the shipment has already left.
-
Technical mapping errors: Outdated EDI mappings or schema mismatches result in structural errors that prevent successful processing.
-
Retailer-specific rules: Each retailer enforces unique ASN rules. Handling these variations manually is both time-consuming and error-prone.
-
Chargebacks and revenue loss: Retailers impose deductions for ASN errors, and vendors often spend significant resources disputing these penalties.
How iNymbus Helps Automate ASN-Related Deduction Management
iNymbus offers an automated deduction management platform designed for high-volume suppliers facing retail chargebacks, including those tied to ASN compliance. Powered by Robotic Process Automation (RPA), the platform supports more than 40 major retailers and helps suppliers recover revenue while reducing manual workload.
What Makes iNymbus Different:
-
End-to-end claim automation: iNymbus handles the entire dispute process, from downloading chargebacks to uploading disputes and documentation.
-
Document retrieval: Collects and organizes ASN records, proof of delivery, carrier data, and EDI acknowledgments without manual intervention.
-
Retailer-specific rules engine: Applies retailer-specific ASN dispute logic, improving accuracy and recovery success rates.
-
Root cause analytics: Dashboards and reports highlight recurring ASN errors, enabling suppliers to address underlying issues and reduce future chargebacks.
-
Custom workflow configuration: Flexible setup adapts to company-specific processes, approval flows, and internal controls.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What happens if I submit an ASN late to Walmart or Amazon?
Late ASNs typically lead to chargebacks or rejected shipments. Both retailers expect the ASN to be received and acknowledged before the goods arrive at their facilities.
What are the common causes of ASN errors?
Discrepancies between listed and actual item quantities, missing UPCs, invalid GLNs, and incorrect packaging structures are among the most common.
Can ASN errors be disputed?
Yes, but the process is manual and time-consuming. Many suppliers use automation platforms like iNymbus to streamline disputes and gather supporting documents.
Does every retailer require an ASN?
Not all retailers require ASNs, but most major ones like Walmart, Amazon, Target, and Costco do. The format and requirements vary by retailer.
How can I reduce ASN-related chargebacks?
Implement automated EDI integration, perform regular audits, monitor retailer acknowledgments, and use analytics to track ASN error trends.
Ready to Eliminate ASN-Related Chargebacks?
iNymbus helps suppliers eliminate costly ASN errors and recover lost revenue by automating the entire deduction dispute process. Whether your claims come through Retail Link, Vendor Central, or email, we are built to scale with your business.
Contact us today to schedule a demo or learn how our automated deduction management solution can reduce your ASN chargeback exposure.








.jpg)
