Walmart, one of the largest retailers in the world, uses a detailed system of deduction codes to effectively manage deductions from vendor payments. These codes address issues such as vendor errors, non-compliance, and other discrepancies, helping maintain efficiency and accountability in its supply chain operations.
For vendors working with Walmart, understanding these deduction codes is important to effectively manage disputes and reduce financial impact. This guide provides an overview of Walmart’s deduction codes, their categories, common reasons, and dispute instructions.
What Are Walmart Deductions, and Why Are They Important?
Walmart deductions are financial adjustments applied to supplier invoices when problems occur in the supply chain. They help Walmart manage issues such as shortages, damages, pricing errors, or late deliveries. In simple terms, deductions are Walmart’s way of making sure suppliers meet their commitments and operations stay on track.
For suppliers, deductions may seem frustrating, but they highlight areas that need attention. A shortage means fewer items were delivered than ordered. Damages refer to products that arrive broken or defective. Pricing errors happen when the invoice does not match the purchase order. Late or incomplete deliveries can result in penalties under Walmart’s On-Time In-Full (OTIF) policy.
Suppliers have the ability to dispute deductions they believe are incorrect by submitting supporting documents such as invoices, purchase orders, or proof of delivery. Many suppliers use deduction management tools to make this process faster and recover lost revenue.
Here are Walmart deduction codes with explanation, and a table overview is provided at the end.
Walmart Deduction Codes: A Complete Breakdown
Code 1: Defective
Definition: Applied when merchandise is received but is found to be defective, including damaged items, malfunctioning products, or those not meeting Walmart’s quality standards.
Example: Walmart receives 200 smartphones, but 20 have non-functioning screens. These defective units are recorded under Code 1.
Dispute Documents: Quality Control Records, Photo Evidence, Proof of Delivery (POD), Bill of Lading (BOL), Packing Lists.
Code 2: Return Recall
Definition: Used when products are recalled by the supplier due to safety, quality, or regulatory issues, or when Walmart initiates a return for similar reasons.
Example: A supplier recalls a line of smartwatches because of a battery defect. Walmart removes the product from shelves and records it under Code 2.
Dispute Documents: Recall Notice, Invoice, Communication with Walmart.
Code 3: Unsellable Merchandise
Definition: Applied when Walmart receives products that cannot be sold due to quality, safety, or compliance issues.
Example: A shipment of canned food arrives with dented and leaking cans. These are marked as unsellable under Code 3.
Dispute Documents: Proof of Delivery (POD), Quality Inspection Reports, Photos, Invoice.
Code 10: Price Difference as Documented
Definition: Triggered when allowances, discounts, or rebates shown on the invoice do not match the purchase order (PO).
Example: A PO specifies a 10% promotional discount, but the supplier’s invoice only applies 5%. This discrepancy generates a Code 10.
Dispute Documents: Supplier Agreement, Purchase Order (PO), Invoice.
Code 11: Price Difference Between PO & Invoice
Definition: Used when the unit cost on the invoice is different from the price on the purchase order.
Example: Walmart orders laptops at $800 each (per PO), but the supplier invoices them at $850. A Code 11 is issued.
Dispute Documents: Invoice, Purchase Order (PO), Contract or Pricing Agreement.
Code 12: Invoice Incorrectly Totaled/Extended
Definition: Applied when mathematical errors are found on the invoice, such as incorrect totals or extensions.
Example: An invoice for 100 units at $10 each is incorrectly totaled as $1,200 instead of $1,000. Walmart flags this with Code 12.
Dispute Documents: Corrected Invoice, Purchase Order (PO), Pricing Agreement.
Code 13: Substitution Overcharge
Definition: Issued when a substituted product is billed at a higher cost than the original agreed product.
Example: Walmart orders generic batteries at $2 each, but the supplier substitutes branded batteries and invoices them at $3 each without approval. A Code 13 is created.
Dispute Documents: Purchase Order (PO), Invoice, Supplier Agreement, Proof of Substitution Approval (if available).
Code 14: Short/Damaged (Trailer Seal Intact)
Definition: Applied when a shipment arrives with shortages or damages, but the trailer seal is still intact, suggesting errors before loading.
Example: Walmart receives a sealed trailer with 500 cartons listed on the BOL, but only 480 are inside. Code 14 documents the shortage.
Dispute Documents: Proof of Delivery (POD), Bill of Lading (BOL), Seal Record, Packing Lists.
Code 15: Pallets/Shrink-Wrapped Short or Damaged
Definition: Used when shrink-wrapped pallets or individual pallets arrive damaged or missing items.
Example: A furniture shipment arrives with several pallets crushed during transit. The damage is recorded under Code 15.
Dispute Documents: Proof of Delivery (POD), Bill of Lading (BOL), Photos, Packing Lists.
Code 20: Concealed Damage
Definition: Applied when damage to merchandise is not visible at the time of delivery but is discovered later when cartons or vendor packs are opened.
Example: A sealed pallet of televisions appears fine on delivery. Later, when unpacked, several screens are found cracked. Walmart records this under Code 20.
Dispute Documents: Proof of Delivery (POD), Bill of Lading (BOL), Photos of Damage, Purchase Order (PO).
Code 21: Concealed Shortage
Definition: Used when a shortage is not visible during receipt but discovered later when the shipment is unpacked or delivered to the store.
Example: A sealed case of shampoo arrives intact, but when opened, it contains only 10 bottles instead of the 12 listed on the PO. This is logged as Code 21.
Dispute Documents: Purchase Order (PO), Proof of Delivery (POD), Bill of Lading (BOL), Invoice.
Code 22: Merchandise Billed Not Shipped
Definition: Occurs when Walmart is billed for items listed on the invoice but does not receive them in the shipment.
Example: A supplier invoices Walmart for 50 laptops, but only 45 are delivered. The missing 5 are documented under Code 22.
Dispute Documents: Purchase Order (PO), Proof of Delivery (POD), Bill of Lading (BOL), Invoice.
Code 23: Carton Shortage (SL&C)
Definition: Applied when there are shortages in shipments loaded and counted at the shipper’s facility (Shipper Load and Count).
Example: A Bill of Lading indicates 500 cartons were loaded, but Walmart only receives 495 cartons. This discrepancy is logged as Code 23.
Dispute Documents: Shipper Load and Count Record, Proof of Delivery (POD), Bill of Lading (BOL), Packing List.
Code 24: Carton Shortage / Freight Bill Signed Short
Definition: Used when the Bill of Lading shows more cartons than Walmart actually receives, and the Proof of Delivery (POD) is signed short.
Example: A delivery shows 30 cartons of televisions on the Bill of Lading, but Walmart receives only 25. The POD is signed short, and Code 24 is issued.
Dispute Documents: Shortage Stamp or Drop Trailer Stamp, Purchase Order (PO), Proof of Delivery (POD), Bill of Lading (BOL), Invoice.
Code 25: No Merchandise Received for Invoice
Definition: Triggered when an invoice is issued, but Walmart does not receive any merchandise tied to it.
Example: A supplier submits an invoice for a shipment of 200 items, but no shipment ever arrives at Walmart. This generates a Code 25.
Dispute Documents: Purchase Order (PO), Proof of Delivery (POD), Bill of Lading (BOL), Invoice.
Code 26: Carton Shortage – Misrouting Changed FOB
Definition: Applied when carton shortages occur due to misrouting in transit, often linked to a change in freight-on-board (FOB) terms.
Example: A shipment of clothing is rerouted during transit. Walmart receives fewer cartons than listed, and the discrepancy is recorded under Code 26.
Dispute Documents: Routing Instructions, Purchase Order (PO), Proof of Delivery (POD), Bill of Lading (BOL).
Code 27: Carton Damage – SL&C
Definition: Used when cartons are damaged during shipping from the supplier’s facility (Shipper Load and Count).
Example: Walmart receives a shipment of kitchen appliances, but several cartons show water damage even though they were sealed. Code 27 is issued.
Dispute Documents: Proof of Delivery (POD), Bill of Lading (BOL), Photos, Packing List.
Code 28: Carton Damage – Freight Bill Signed Damaged
Definition: Applied when a shipment is received with visible carton damage, noted at the time of delivery and signed as damaged on the freight bill.
Example: A Walmart distribution center receives a truckload of TVs with multiple cartons visibly crushed. The POD is signed “damaged,” and Code 28 is applied.
Dispute Documents: Freight Bill Signed “Damaged,” Proof of Delivery (POD), Bill of Lading (BOL), Photos.
Code 29: Carton Damage – Misrouting Changed FOB
Definition: Applied when carton damage occurs as a result of misrouting in transit, typically tied to freight-on-board (FOB) term changes.
Example: A rerouted shipment of bicycles arrives with damaged cartons due to extended handling. Walmart issues a Code 29.
Dispute Documents: Routing Documentation, Proof of Delivery (POD), Bill of Lading (BOL), Photos.
Code 30: Duplicate Billing
Definition: Applied when Walmart receives multiple invoices for the same merchandise or shipment.
Example: A supplier sends two invoices for the same PO of 100 refrigerators. Walmart flags this duplication under Code 30.
Dispute Documents: Original Invoice, Duplicate Invoice, Purchase Order (PO), Proof of Delivery (POD).
Code 31: PO Number Not on Invoice
Definition: Issued when the purchase order (PO) number is missing from the supplier’s invoice.
Example: A supplier submits an invoice for a shipment of shoes, but it does not include the PO number. Walmart records this under Code 31.
Dispute Documents: Corrected Invoice with PO, Original Invoice, Purchase Order (PO).
Code 32: Multiple PO Numbers on Invoice
Definition: Applied when an invoice incorrectly references more than one purchase order.
Example: A supplier invoices Walmart for two separate POs (furniture and electronics) on the same invoice. Walmart issues a Code 32.
Dispute Documents: Separate Corrected Invoices, Original Invoice, Purchase Orders (POs).
Code 33: PO Number Incorrect on Invoice
Definition: Used when the PO number listed on the invoice does not match Walmart’s actual PO.
Example: Walmart issues PO #5678, but the supplier’s invoice references PO #5679. Walmart records this under Code 33.
Dispute Documents: Corrected Invoice, Original Invoice, Purchase Order (PO).
Code 34: Pallet Charge
Definition: Applied when suppliers add unauthorized pallet charges to an invoice.
Example: A supplier invoices Walmart an extra $200 for pallets that were not part of the agreement. Walmart deducts this amount under Code 34.
Dispute Documents: Invoice, Supplier Agreement, Purchase Order (PO).
Code 35: Sales Tax – State
Definition: Used when state sales tax is charged incorrectly or in excess on an invoice.
Example: A supplier charges state sales tax to a Walmart DC located in a tax-exempt state. Walmart issues a Code 35.
Dispute Documents: Invoice, Tax Exemption Certificate, Purchase Order (PO).
Code 36: Sales Tax – City
Definition: Applied when city sales tax is incorrectly added to an invoice.
Example: A supplier adds city sales tax for a location where Walmart is exempt. Walmart records this as Code 36.
Dispute Documents: Invoice, Tax Exemption Certificate, Purchase Order (PO).
Code 37: Insurance
Definition: Applied when unauthorized insurance charges appear on a supplier invoice.
Example: A supplier invoices Walmart an additional $50 per shipment for insurance, though the contract terms specify prepaid freight. Walmart deducts this under Code 37.
Dispute Documents: Invoice, Supplier Agreement, Purchase Order (PO).
Code 38: Stop-Off Charge Incorrectly Added
Definition: Issued when suppliers add unauthorized stop-off charges to an invoice.
Example: A supplier invoices Walmart for an additional stop at a secondary warehouse, even though Walmart did not request it. Walmart issues Code 38.
Dispute Documents: Invoice, Routing Guide, Purchase Order (PO).
Code 39: Freight Cost on Backorder
Definition: Applied when freight charges are incorrectly billed on backordered shipments.
Example: A supplier invoices Walmart for freight charges on backordered kitchen appliances, which should not incur additional freight. Walmart deducts this under Code 39.
Dispute Documents: Invoice, Purchase Order (PO), Routing Agreement.
Code 40: Routing Violation – Excessive Freight
Definition: Applied when suppliers fail to follow Walmart’s routing guide, resulting in excessive freight charges.
Example: A supplier ships via an unauthorized carrier that charges higher rates than Walmart’s approved routing instructions. The excess cost is deducted under Code 40.
Dispute Documents: Invoice, Walmart Routing Guide, Proof of Delivery (POD), Bill of Lading (BOL).
Code 41: Collect – Should Have Been Prepaid
Definition: Issued when freight charges are incorrectly billed as collect instead of prepaid, as required by Walmart’s terms.
Example: A shipment of toys arrives marked freight collect, but the agreement required prepaid freight. Walmart issues Code 41.
Dispute Documents: Freight Terms Agreement, Invoice, Bill of Lading (BOL), Purchase Order (PO).
Code 42: Backhaul / Pickup Allowance
Definition: Applied when suppliers fail to account for backhaul or pickup allowances that were agreed upon in the supplier contract.
Example: Walmart’s agreement states that freight costs are reduced by $300 due to backhaul, but the invoice does not reflect this deduction. Walmart records Code 42.
Dispute Documents: Supplier Agreement, Invoice, Routing Guide.
Code 43: Merchandise Should Be Prepaid to Consolidator
Definition: Issued when freight charges are billed to Walmart, even though merchandise should have been shipped prepaid to a consolidator.
Example: A supplier sends freight charges for goods that should have been prepaid to Walmart’s consolidator. Walmart deducts the expense under Code 43.
Dispute Documents: Invoice, Consolidation Agreement, Bill of Lading (BOL).
Code 44: Freight on Returned Merchandise
Definition: Applied when freight charges are incorrectly billed to Walmart for returned merchandise.
Example: A supplier invoices Walmart for return freight on recalled merchandise. Walmart flags this as Code 44.
Dispute Documents: Invoice, Return Agreement, Bill of Lading (BOL), Proof of Return Authorization.
Code 45: Prepaid Freight Incorrectly Added to Invoice
Definition: Issued when suppliers incorrectly add prepaid freight charges to an invoice.
Example: Walmart’s terms state “FOB Destination, freight prepaid,” but the supplier invoices Walmart separately for freight. Walmart issues Code 45.
Dispute Documents: Supplier Agreement, Invoice, Purchase Order (PO).
Code 46: Freight Allowance
Definition: Applied when agreed freight allowances are not reflected on the invoice.
Example: Walmart negotiated a $500 freight allowance, but the supplier invoices the full shipping cost. The difference is deducted under Code 46.
Dispute Documents: Supplier Agreement, Invoice, Purchase Order (PO).
Code 47: Excessive Freight Charge on Invoice
Definition: Used when freight charges on an invoice exceed the agreed or reasonable amount.
Example: A shipment’s agreed freight rate is $1,000, but the supplier invoices Walmart $1,500. Walmart issues Code 47.
Dispute Documents: Invoice, Freight Rate Agreement, Routing Guide.
Code 48: Freight Should Be Prepaid to Consolidator
Definition: Applied when freight charges are incorrectly billed to Walmart for shipments that should have been prepaid to the consolidator.
Example: A supplier invoices Walmart for freight costs, even though the terms specify prepaid freight to Walmart’s consolidator. Walmart records this under Code 48.
Dispute Documents: Invoice, Bill of Lading (BOL), Consolidation Agreement.
Code 49: Freight Cost to Forward Misrouted Shipment
Definition: Issued when Walmart incurs freight charges to correct misrouted shipments caused by supplier error.
Example: A supplier ships goods to the wrong distribution center. Walmart pays to forward the shipment to the correct location and deducts the cost under Code 49.
Dispute Documents: Invoice, Bill of Lading (BOL), Routing Instructions, Proof of Delivery (POD).
Code 50: Advertising Allowance
Definition: Applied when advertising allowances agreed upon between Walmart and the supplier are not properly reflected or documented.
Example: Walmart and a supplier agree to a $5,000 advertising allowance for a seasonal campaign, but the supplier’s invoice does not apply the allowance. Walmart issues Code 50.
Dispute Documents: Supplier Agreement, Marketing Contract, Invoice.
Code 51: Promotional Allowance Display / Fixture Allowance
Definition: Issued when allowances for promotional displays or fixtures are not properly executed or documented.
Example: A supplier agrees to provide an in-store promotional display at a discounted cost, but the invoice shows full price. Walmart records this under Code 51.
Dispute Documents: Agreement, Invoice, Purchase Order (PO).
Code 52: Volume Allowance
Definition: Applied when volume-based discounts agreed with Walmart are not reflected on the invoice.
Example: A supplier promises a 10% volume discount for orders over 10,000 units, but Walmart’s invoice shows full price. Walmart deducts the difference under Code 52.
Dispute Documents: Supplier Agreement, Invoice, Purchase Order (PO).
Code 53: Truckload Allowance
Definition: Used when negotiated truckload allowances are missing or incorrectly applied on an invoice.
Example: A supplier agrees to reduce freight costs by $1,000 for full truckload shipments, but Walmart is billed the full amount. Walmart issues Code 53.
Dispute Documents: Supplier Agreement, Invoice, Freight Contract.
Code 54: Warehouse Allowance
Definition: Applied when agreed warehouse allowances are not included in invoicing.
Example: A supplier agrees to a $2,000 warehouse handling allowance but invoices Walmart the full amount without the deduction. Walmart records this under Code 54.
Dispute Documents: Warehouse Agreement, Invoice, Purchase Order (PO).
Code 55: New Location Allowance
Definition: Issued when allowances for new locations are not documented or deducted properly on invoices.
Example: A supplier agrees to a $500 allowance per store opening but invoices Walmart the full amount without applying the allowance. Walmart issues Code 55.
Dispute Documents: Agreement, Invoice, Purchase Order (PO).
Code 56: Allowance Not Given Off Invoice
Definition: Applied when agreed allowances (rebates, discounts, or incentives) are not taken off the invoice as required.
Example: Walmart negotiates a $1 per unit allowance on a seasonal product, but the supplier invoices at full price. Walmart records Code 56.
Dispute Documents: Supplier Agreement, Invoice, Purchase Order (PO).
Code 57: Quantity Discount
Definition: Used when agreed quantity-based discounts are missing from an invoice.
Example: A supplier agrees to a 15% discount on orders above 5,000 units, but Walmart’s invoice shows standard pricing. Code 57 is applied.
Dispute Documents: Pricing Agreement, Invoice, Purchase Order (PO).
Code 58: Other Allowances
Definition: Applied for allowance-related deductions not covered by specific codes.
Example: Walmart and a supplier agree to a seasonal allowance for promotional packaging, but the supplier fails to apply it to the invoice. Walmart records Code 58.
Dispute Documents: Agreement, Invoice, Purchase Order (PO).
Code 59: Defective Merchandise Allowance
Definition: Issued when defective merchandise allowances are not properly applied or documented on invoices.
Example: A supplier agrees to a 5% allowance for defective returns, but Walmart’s invoice reflects full charges. Walmart issues Code 59.
Dispute Documents: Supplier Agreement, Invoice, Return Documentation.
Code 60: Handling Charge as Documented
Definition: Applied when handling charges are incorrectly added to an invoice or differ from the agreed terms.
Example: A supplier adds a $200 handling fee to Walmart’s invoice, even though the supplier agreement specifies that handling is included. Walmart issues Code 60.
Dispute Documents: Supplier Agreement, Invoice, Purchase Order (PO).
Code 61: Incorrect Color or Size Allowance
Definition: Issued when products do not match the size or color specifications outlined in the purchase order.
Example: Walmart orders 1,000 blue T-shirts in size medium, but the supplier ships red T-shirts in size large. This discrepancy is recorded under Code 61.
Dispute Documents: Purchase Order (PO), Packing List, Invoice.
Code 62: Labor and Handling
Definition: Applied when unauthorized labor or handling charges are billed to Walmart.
Example: A supplier invoices Walmart for an additional $500 in “special handling fees” that were not part of the agreement. Walmart deducts this under Code 62.
Dispute Documents: Invoice, Supplier Agreement, Purchase Order (PO).
Code 63: Bill of Lading Addressed to Wrong Location
Definition: Used when the Bill of Lading (BOL) lists the wrong delivery address or Walmart facility.
Example: A shipment meant for Walmart’s Dallas distribution center is addressed to the Houston DC. Walmart records this under Code 63.
Dispute Documents: Corrected Bill of Lading (BOL), Invoice, Routing Instructions.
Code 64: Early Shipment
Definition: Applied when merchandise is delivered earlier than the agreed ship or delivery window.
Example: A supplier delivers a holiday toy shipment two weeks early, creating storage issues at Walmart’s DC. Walmart issues Code 64.
Dispute Documents: Purchase Order (PO), Proof of Delivery (POD), Bill of Lading (BOL).
Code 65: Late Shipment
Definition: Issued when merchandise arrives later than the delivery window specified in Walmart’s purchase order.
Example: A shipment of grocery items scheduled for delivery on June 1 arrives on June 5. Walmart deducts penalties under Code 65.
Dispute Documents: Purchase Order (PO), Proof of Delivery (POD), Bill of Lading (BOL).
Code 66: No PO Number on Carton
Definition: Applied when cartons in a shipment are missing the required purchase order number.
Example: A supplier sends multiple cartons of electronics without PO numbers printed on the labels. Walmart records this under Code 66.
Dispute Documents: Packing List, Corrected Carton Labels, Purchase Order (PO).
Code 67: Incorrect PO Number on Carton
Definition: Issued when cartons are labeled with the wrong PO number.
Example: Walmart issues PO #1234 for a shipment, but cartons are labeled with PO #4321. Walmart records this under Code 67.
Dispute Documents: Packing List, Corrected Labels, Purchase Order (PO).
Code 68: PO Number Not on Bill of Lading
Definition: Used when the Bill of Lading does not include the required PO number.
Example: A truckload of clothing arrives with a Bill of Lading missing the Walmart PO number. This is logged under Code 68.
Dispute Documents: Corrected Bill of Lading (BOL), Purchase Order (PO), Invoice.
Code 69: Incorrect PO Number on Bill of Lading
Definition: Applied when the PO number on the Bill of Lading does not match the Walmart purchase order.
Example: Walmart issues PO #5678, but the Bill of Lading lists PO #8765. Walmart issues Code 69 to document the discrepancy.
Dispute Documents: Corrected Bill of Lading (BOL), Purchase Order (PO), Invoice.
Code 70: No Item Number on Cartons
Definition: Applied when cartons are shipped without Walmart item numbers printed on them, making identification difficult.
Example: A supplier delivers 500 cartons of apparel, but none of the cartons include the required Walmart item numbers. Walmart issues Code 70.
Dispute Documents: Packing List, Corrected Carton Labels, Purchase Order (PO).
Code 71: Incorrect Item Number on Cartons
Definition: Issued when cartons are labeled with an incorrect Walmart item number.
Example: A shipment of jeans is labeled with an item number for jackets. Walmart flags this under Code 71.
Dispute Documents: Packing List, Corrected Carton Labels, Purchase Order (PO).
Code 72: Labor and Handling
Definition: Applied when unauthorized labor or handling fees are billed on an invoice.
Example: A supplier adds $400 in “special labor fees” to Walmart’s invoice, even though the supplier agreement does not allow for these charges. Walmart records this as Code 72.
Dispute Documents: Invoice, Supplier Agreement, Purchase Order (PO).
Code 73: Duplicate Payment
Definition: Issued when Walmart identifies a duplicate payment made to the supplier. The deduction reverses the overpayment.
Example: Walmart accidentally pays a supplier twice for the same $10,000 invoice. The second payment is recovered under Code 73.
Dispute Documents: Duplicate Invoices, Payment Records, Purchase Order (PO).
Code 74: Previous Account – Debit Balance
Definition: Applied when an outstanding debit balance from a prior account is transferred and deducted from the supplier.
Example: A supplier merges accounts, but a $2,000 debit balance from the old account is carried forward. Walmart deducts this under Code 74.
Dispute Documents: Account Reconciliation Statement, Invoice Records, Debit Balance Documentation.
Code 75: Transfer of Debit Balance
Definition: Used when debit balances are transferred between accounts and applied to current transactions.
Example: A $500 debit from one supplier account is transferred to a consolidated account. Walmart issues Code 75.
Dispute Documents: Account Statements, Debit Balance Documentation, Payment Records.
Code 76: Buyer’s Reserve
Definition: Applied when Walmart withholds payment for reserve funds set aside by the buyer for specific purposes (such as claims, reserves, or offsets).
Example: Walmart places a reserve holdback of $1,000 from a supplier payment as outlined in the supplier agreement. This is recorded under Code 76.
Dispute Documents: Supplier Agreement, Invoice, Reserve Documentation.
Code 77: Overpayment of Invoice Amount
Definition: Issued when Walmart identifies that an invoice was overpaid and deducts the overpaid amount.
Example: A supplier invoices $8,500, but Walmart mistakenly pays $9,000. The $500 difference is recovered under Code 77.
Dispute Documents: Invoice, Payment Records, Credit/Debit Notes.
Code 78: Storage Charges
Definition: Applied when suppliers charge Walmart storage fees that are not authorized in the agreement.
Example: A supplier invoices Walmart an extra $250 for “warehouse storage fees,” though storage was not part of the agreement. Walmart deducts this as Code 78.
Dispute Documents: Supplier Agreement, Invoice, Purchase Order (PO).
Code 79: Sample Charges
Definition: Issued when suppliers bill Walmart for product samples that should have been provided at no cost.
Example: A supplier charges Walmart $150 for clothing samples provided during a product review. Walmart records this deduction under Code 79.
Dispute Documents: Supplier Agreement, Invoice, Correspondence (if samples were requested).
Code 80: Cash Discount
Definition: Applied when suppliers fail to honor agreed cash discounts for early or timely payments.
Example: Walmart pays a supplier within 10 days under a 2% cash discount agreement, but the supplier invoices the full amount. Walmart deducts the 2% under Code 80.
Dispute Documents: Supplier Agreement, Invoice, Payment Records.
Code 81: Anticipation – Vendor Request
Definition: Issued when vendors request early payment and related anticipation charges are incorrectly applied.
Example: A supplier asks Walmart to pay 30 days early and adds an anticipation fee to the invoice. Walmart records this under Code 81.
Dispute Documents: Supplier Request Documentation, Invoice, Payment Agreement.
Code 82: Anticipation – Early Payment of Invoice
Definition: Applied when early payment anticipation discounts are not properly deducted on invoices.
Example: Walmart pays an invoice 30 days early under agreed anticipation terms, but the discount is not applied. Walmart issues Code 82.
Dispute Documents: Payment Records, Supplier Agreement, Invoice.
Code 83: Discount Not Taken at Time of Payment
Definition: Used when negotiated discounts are missed during payment processing and later deducted.
Example: Walmart is entitled to a 3% discount for payment within 15 days but accidentally pays the full amount. The discount is later deducted under Code 83.
Dispute Documents: Supplier Agreement, Invoice, Payment Records.
Code 84: Interest on Recovery of Payment in Error
Definition: Applied when Walmart deducts interest charges tied to recovering erroneous overpayments.
Example: Walmart discovers a $10,000 overpayment and deducts not only the overpayment but also interest accrued. This is logged as Code 84.
Dispute Documents: Payment Records, Overpayment Documentation, Agreement Terms.
Code 85: Interest on Overpayment
Definition: Issued when Walmart charges suppliers interest on overpaid amounts held by the supplier.
Example: A supplier receives $2,000 more than invoiced and holds the funds for several weeks. Walmart deducts interest under Code 85.
Dispute Documents: Payment Records, Overpayment Documentation, Supplier Agreement.
Code 86: Excise Tax
Definition: Applied when excise taxes are incorrectly charged or not in compliance with Walmart’s agreements.
Example: A supplier adds excise tax to beverage shipments where Walmart is exempt. Walmart issues Code 86.
Dispute Documents: Invoice, Tax Certificates, Purchase Order (PO).
Code 87: Other
Definition: Used for miscellaneous or uncategorized deductions that do not fall under standard codes.
Example: A supplier charges Walmart a one-time administrative fee not listed in the agreement. Walmart deducts this as Code 87.
Dispute Documents: Invoice, Supplier Agreement, Supporting Documentation.
Code 90: Unauthorized Charge – System Deduction
Definition: Applied when Walmart identifies charges on an invoice that were not authorized or agreed upon.
Example: A supplier adds a $250 “documentation fee” to an invoice without Walmart’s approval. Walmart removes the charge under Code 90.
Dispute Documents: Supplier Agreement, Invoice, Purchase Order (PO), Communication Records.
Code 91: Merchandise Destroyed – Damaged/Defective
Definition: Used when merchandise is destroyed due to being damaged or defective beyond repair.
Example: A shipment of frozen foods arrives spoiled due to improper refrigeration. Walmart disposes of the goods and records Code 91.
Dispute Documents: Proof of Destruction, Quality Control Report, Invoice, Proof of Delivery (POD).
Code 92: Merchandise Return – Overstock/Recall
Definition: Applied when Walmart returns merchandise due to overstock situations or supplier recalls.
Example: A supplier recalls 5,000 baby strollers due to safety concerns, and Walmart returns its inventory under Code 92.
Dispute Documents: Recall Notice, Return Authorization, Invoice, Purchase Order (PO).
Code 93: Merchandise Return – Damaged Merchandise
Definition: Issued when Walmart returns merchandise that was received in a damaged condition.
Example: A shipment of televisions arrives with cracked screens. Walmart returns the damaged units under Code 93.
Dispute Documents: Return Authorization, Proof of Delivery (POD), Bill of Lading (BOL), Invoice.
Code 94: Merchandise Return – Defective Merchandise
Definition: Applied when Walmart returns merchandise that is defective but not visibly damaged.
Example: A batch of small kitchen appliances malfunctions during testing. Walmart returns them under Code 94.
Dispute Documents: Return Authorization, Quality Reports, Invoice, Purchase Order (PO).
Code 95: Merchandise Return – Wrong Item
Definition: Used when Walmart receives the wrong item compared to the purchase order and returns it.
Example: Walmart orders 200 printers but receives 200 scanners instead. The items are returned under Code 95.
Dispute Documents: Return Authorization, Purchase Order (PO), Invoice, Proof of Delivery (POD).
Code 96: Merchandise for Repair/Assembly – Not Returned
Definition: Applied when merchandise sent for repair or assembly is not returned by the supplier.
Example: Walmart sends 100 laptops to a supplier for repair, but the items are never returned. Walmart issues Code 96.
Dispute Documents: Repair Agreement, Return Documentation, Invoice.
Code 97: Returned Merchandise Handling Charge
Definition: Issued when handling charges for returned merchandise are not agreed upon or incorrectly billed.
Example: A supplier invoices Walmart $500 for handling returned merchandise, even though the contract states that returns are handled at no cost. Walmart deducts this under Code 97.
Dispute Documents: Supplier Agreement, Invoice, Return Authorization.
Code 99: On-Time In-Full (OTIF)
Definition: Applied when shipments fail to meet Walmart’s On-Time In-Full requirements, such as late deliveries, partial shipments, or missing items.
Example: Walmart orders 500 units of a seasonal product for delivery on August 1. The supplier delivers 450 units on August 3. Walmart records this failure under Code 99.
Dispute Documents: Proof of Delivery (POD), Bill of Lading (BOL), Purchase Order (PO).
How to Dispute Walmart Deduction Codes On Walmart APDP
Walmart APDP > Create Dispute > Enter Required Details (Vendor Code| Claim Code) > Click Search
You will a similar screen.
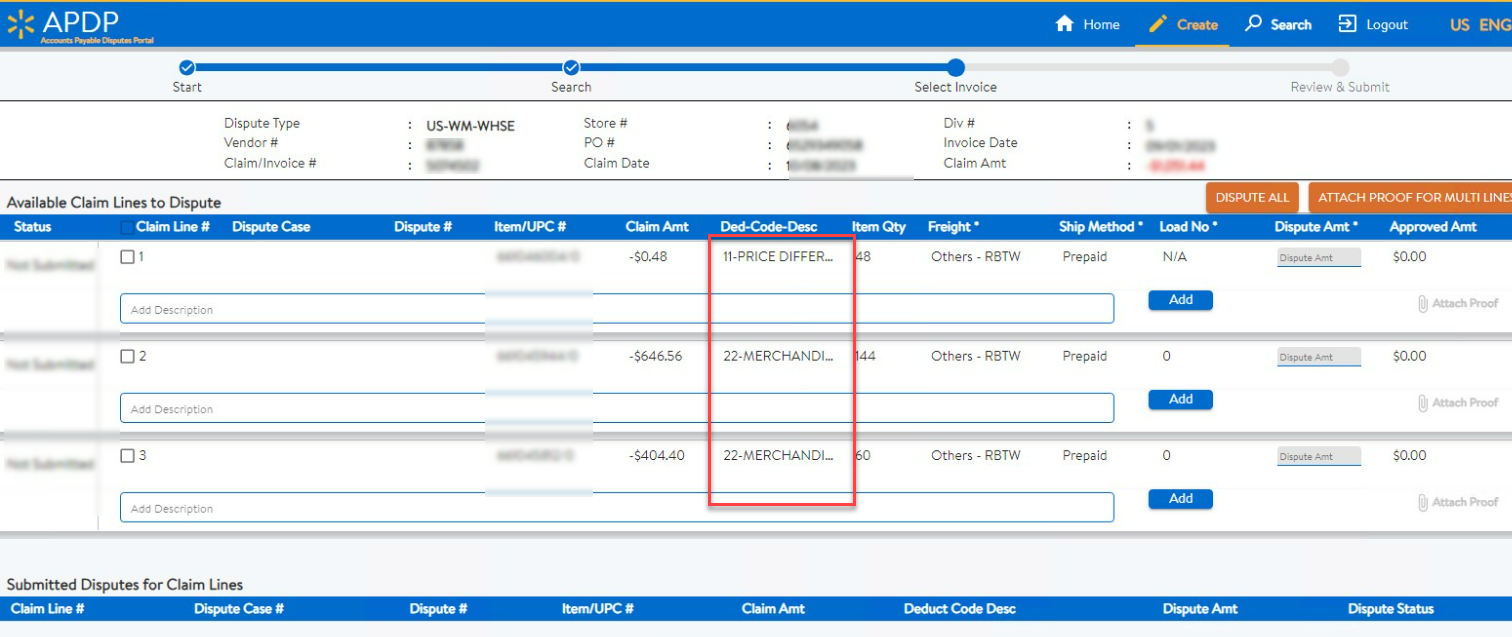
Check our blog on “Walmart Deduction Recovery: Disputing Claims On APDP”
Complete Walmart Deduction Codes List
To help you navigate Walmart deduction codes effectively, we've compiled a comprehensive table, along with their descriptions and typical reasons for application. Please refer to this table as a quick reference guide:
|
Walmart Code |
EDI |
Definition |
|
1 |
F1 |
Defective |
|
2 |
15 |
Return recall |
|
3 |
GG |
Unsellable merchandise |
|
10 |
1 |
Price Difference as Documented |
|
11 |
1 |
Price Difference between PO & Invoice |
|
12 |
3 |
Invoice Incorrectly Totaled/Extended |
|
13 |
A5 |
Substitution Overcharge |
|
14 |
6 |
Short/Damaged (Trailer Seal Intact) |
|
15 |
6 |
Pallets/Shrink-wrapped Short/Damaged |
|
20 |
6 |
Concealed Damage |
|
21 |
6 |
Concealed Shortage |
|
22 |
59 |
Merchandise Billed not Shipped |
|
23 |
6 |
Carton Shortage SL&C |
|
24 |
6 |
Carton Shortage/Freight Bill Signed Short |
|
25 |
A9 |
No Merchandise Received for Invoice |
|
26 |
TI |
Carton Shortage – Misrouting changed FOB |
|
27 |
6 |
Carton Damage – SL&C |
|
28 |
6 |
Carton Damage – Frt. bill signed damaged |
|
29 |
TI |
Carton Damage – Misrouting changed FOB |
|
30 |
19 |
Duplicate Billing |
|
31 |
MH |
PO number not on invoice |
|
32 |
MF |
Multiple PO numbers on invoice |
|
33 |
MG |
PO number incorrect on invoice |
|
34 |
10 |
Pallet charge |
|
35 |
55 |
Sales tax – state |
|
36 |
55 |
Sales tax – city |
|
37 |
DO |
Insurance |
|
38 |
30 |
Stop-off charge incorrectly added |
|
39 |
MC |
Freight cost on backorder |
|
40 |
B8 |
Routing violation – excessive freight |
|
41 |
SO |
Collect – should have been pre-paid |
|
42 |
MB |
Backhaul/pickup allowance |
|
43 |
RJ |
Merchandise S/B prepaid to consolidator |
|
44 |
RL |
Freight on returned merchandise |
|
45 |
21 |
Prepaid freight incorrectly added to invoice |
|
46 |
RB |
Freight allowance |
|
47 |
SF |
Excessive freight charge on invoice |
|
48 |
21 |
Freight should be prepaid to consolidator |
|
49 |
54 |
Freight cost to forward misrouted shipment |
|
50 |
71 |
Advertising allowance |
|
51 |
A8 |
Promotional allowance display/fixture allowance |
|
52 |
D5 |
Volume allowance |
|
53 |
D5 |
Truckload allowance |
|
54 |
ZZ |
Warehouse allowance |
|
55 |
A3 |
New location allowance |
|
56 |
89 |
Allowance not given off invoice |
|
57 |
D5 |
Quantity discount |
|
58 |
OT |
Other allowances |
|
59 |
82 |
Defective merchandise allowance |
|
60 |
97 |
Handling charge as documented |
|
61 |
37 |
Incorrect color/size allowance |
|
62 |
98 |
Labor and handling |
|
63 |
40 |
BOL addressed to wrong location |
|
64 |
RH |
Early shipment |
|
65 |
99 |
Late shipment |
|
66 |
MP |
No PO number on carton |
|
67 |
MN |
Incorrect PO number on carton |
|
68 |
ME |
PO number not on BOL |
|
69 |
MD |
Incorrect PO number on BOL |
|
70 |
MO |
No item number on cartons |
|
71 |
MM |
Incorrect item number on cartons |
|
72 |
C9 |
Labor and handling |
|
73 |
86 |
Duplicate payment |
|
74 |
E1 |
Previous account – debit balance |
|
75 |
MI |
Transfer of debit balance |
|
76 |
C4 |
Buyer’s reserve |
|
77 |
WO |
Overpayment of invoice amount |
|
78 |
MQ |
Storage charges |
|
79 |
GD |
Sample charges |
|
80 |
76 |
Cash discount |
|
81 |
FA |
Anticipation – vendor request |
|
82 |
FA |
Anticipation – early payment of invoice |
|
83 |
D6 |
Discount not taken at time of payment |
|
84 |
L5 |
Interest on recovery of payment in error |
|
85 |
RU |
Interest on overpayment |
|
86 |
55 |
Excise tax |
|
87 |
ZZ |
Other |
|
90 |
D3 |
Unauthorized charge – system deduction |
|
91 |
93 |
Merchandise destroyed – damaged/defective |
|
92 |
15 |
Merchandise return – overstock/recall |
|
93 |
4 |
Merchandise return – damaged merchandise |
|
94 |
F1 |
Merchandise return – defective merchandise |
|
95 |
A2 |
Merchandise return – wrong item |
|
96 |
B5 |
Merchandise for repair/assembly – not returned |
|
97 |
97 |
Returned merchandise handling charge |
|
150 |
82 |
Soft goods defective allowance |
|
151 |
B2 |
Purchase rebate allowance |
|
152 |
28 |
Wholesale club allowance |
|
161 |
B2 |
Purchase rebate allowance |
Managing Walmart Chargeback Codes with iNymbus
Understanding Walmart Chargeback codes is only the first step. Managing deductions requires time, attention to detail, and consistent follow-up, which can be overwhelming for many suppliers.
This is where iNymbus helps. Our solution:
-
Streamlines deduction management so you spend less time on manual tracking
-
Identifies recurring trends to help you address the root causes of chargebacks
-
Automates the dispute process to ensure timely submissions with complete documentation
-
Protects profitability by reducing revenue lost to preventable or invalid deductions
Instead of allowing chargebacks to reduce your margins, you can take control and transform deduction management into a competitive advantage.
Learn how to automate Walmart deduction management with iNymbus and save valuable time and money.






.jpg)
