How do complex supply chains manage to process orders with such precision? The answer lies in Electronic Data Interchange (EDI)—the technology that enables businesses to seamlessly exchange crucial documents like purchase orders and shipping notices.
But here’s the catch: without strict EDI Compliance, even minor mistakes can lead to costly disruptions, chargebacks, and strained relationships with trading partners.
Whether you're a supply chain manager or business owner, this guide will provide valuable insights into EDI Compliance.
What is EDI Compliance?
EDI compliance refers to the adherence to specific electronic data interchange standards and formats, usually set by trading partners. These standards define how business documents are structured and exchanged, ensuring that all parties can accurately interpret the data being transmitted. EDI compliance minimizes misunderstandings, reduces manual processes, and helps streamline the flow of information between companies.
EDI Compliance Requirements
To be considered EDI compliant, a business must meet the specific requirements set by each trading partner. These requirements can vary significantly depending on the partner’s industry, size, and individual needs. Businesses must be familiar with and able to accommodate the necessary document types, exchange protocols, and security standards
Common EDI Standards and Formats
Just like different countries have different languages, different industries and regions use different EDI "languages" (standards). Here are a few important ones:
-
ANSI X12: Widely used in North America, the ANSI X12 standard covers industries like finance, transportation, healthcare, and retail. For suppliers working with U.S.-based retailers, this is the most common EDI format.
-
EDIFACT: An international EDI standard developed by the United Nations, more commonly used in Europe and Asia. It is widely adopted by global companies to ensure interoperability across borders.
-
XML (eXtensible Markup Language): While not a traditional EDI standard, XML has become increasingly popular due to its flexibility and compatibility with various systems. XML is often used alongside or as a replacement for traditional EDI formats in certain industries.
Trading Partner Requirements and Specific Needs to Become EDI Compliant
Major retailers like Amazon, Walmart, and Target each have their own unique EDI requirements that suppliers must adhere to in order to maintain their business relationships.
Amazon EDI Compliance Requirements:
Vendor Central Account: Vendors must have an Amazon Vendor Central account and access to EDI Self-Service Startup.
EDI Version: Amazon requires version 4010 or higher.
Timeliness: Purchase orders must be transmitted within 8 hours, advance shipment notices must be sent 4 hours before arrival, and invoices should be submitted within 24 hours of shipment confirmation.
Communication Protocol: Amazon primarily uses AS2 over HTTPS for secure data exchange.
Walmart EDI Compliance Requirements:
Access to Retail Link: Suppliers must obtain access to Walmart's Retail Link platform, which provides necessary documentation and guidelines for EDI compliance
EDI Compliance: Suppliers must fully comply with Walmart’s EDI standards before starting any trading.
Communication Protocols: Walmart supports secure communication via AS2 or a Value-Added Network (VAN).
Testing and Certification: Suppliers must undergo testing to ensure their systems can communicate with Walmart’s systems effectively.
Overview of Common EDI Transactions
-
EDI 850: Purchase Order – Initiates the purchase process with product details and pricing.
-
EDI 855: Purchase Order Acknowledgment – Confirms the purchase order details.
-
EDI 856: Advance Shipment Notice (ASN) – Provides shipment details to the buyer.
-
EDI 810: Invoice – Requests payment for goods or services.
-
EDI 997: Functional Acknowledgment – Confirms receipt of EDI documents and highlights any errors.
-
EDI 846: Inventory Inquiry/Advice – Updates on product availability and stock levels.
-
EDI 940: Warehouse Shipping Order – Directs third-party warehouses to ship goods.
-
EDI 945: Warehouse Shipping Advice – Confirms shipment details from the warehouse.
-
EDI 832: Price/Sales Catalog – Communicates product pricing and updates.
-
EDI 820: Payment Order/Remittance Advice – Authorizes payments and provides remittance details.
The Role of EDI in Retail
EDI has become essential for retailers looking to automate and streamline document exchanges. Here’s how it benefits the retail sector:
-
Faster Order Processing: Automation helps retailers process orders quickly, improving lead times and customer satisfaction.
-
Error Reduction: By eliminating manual data entry, EDI minimizes errors, ensuring seamless transactions.
-
Cost Reduction: Automation reduces the reliance on paper-based transactions and manual entries, cutting operational costs.
What are EDI Chargebacks?
EDI chargebacks are financial penalties imposed by a trading partner, usually a retailer, when a supplier fails to meet specific EDI requirements. Common reasons for chargebacks include late delivery of documents, incorrect formatting, or mismatched data. While the penalties may seem small, they can accumulate over time, leading to significant financial losses for the supplier.
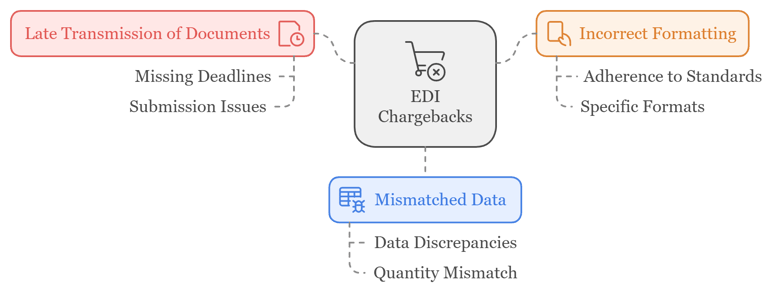
Common Reasons for EDI Chargebacks
-
Late transmission of documents: Missing deadlines for submitting purchase orders, invoices, or advance shipping notices can prompt chargebacks.
-
Incorrect formatting: Failing to adhere to the specific EDI standards or formats set by the trading partner will result in non-compliance penalties.
-
Mismatched data: Data discrepancies between purchase orders, shipping notices, and invoices can lead to chargebacks. For example, if the quantity of goods shipped does not match the purchase order, this could trigger a penalty.
Impact of EDI Chargebacks on Businesses
Chargebacks can have a serious impact on a supplier’s profitability, especially when working with major retailers. The costs associated with frequent chargebacks can quickly reduce profit margins, making it essential to minimize them. Additionally, a consistent pattern of chargebacks can damage the supplier’s relationship with the retailer, potentially leading to fewer business opportunities in the future.
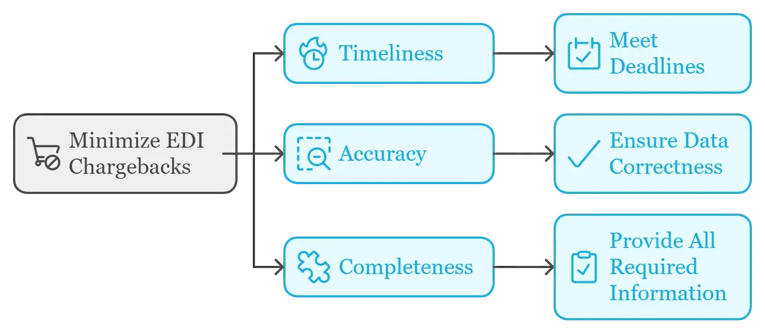
How to Minimize EDI Chargebacks
To minimize EDI chargebacks, businesses must focus on three key areas: timeliness, accuracy, and completeness.
-
Timeliness: Timeliness refers to meeting the deadlines for transmitting EDI documents such as purchase orders, invoices, and advance shipping notices. Failure to send these documents within the specified timeframes can result in late fees or chargebacks.
-
Accuracy: Accuracy ensures that the data exchanged between you and your trading partners is correct. Errors in document details, such as incorrect product quantities, prices, or shipping information, can lead to data mismatches and chargebacks.
- Completeness: Completeness refers to providing all the required information in each EDI document. Missing or incomplete data—such as missing product SKUs, shipping details, or payment terms—can result in chargebacks from trading partners.
Can You Fully Prevent EDI Compliance Chargebacks?
In short, no. Chargebacks related to EDI compliance are often unavoidable due to several factors inherent in the retail environment.
While EDI chargebacks can pose significant challenges to profitability and operational efficiency, iNymbus offers solutions to help vendors manage and mitigate their impact. We understand the complexities suppliers face in maintaining compliance.
Overcome Chargebacks With iNymbus
To fully leverage financial potential, businesses need more than just compliance—they need automation. That’s where iNymbus Deduction Management Software comes in. By utilizing Robotic Process Automation (RPA), iNymbus automates key aspects of the deduction management process, minimizing manual work, errors, and delays.
Key Features of iNymbus Deduction Management Software:
-
Automated Document Retrieval: The system retrieves documents from various sources, including ERP systems, EDI, portals, and emails, without the need for manual intervention. This ensures that all required documents are available for dispute resolution.
-
Fast and Error-Free Dispute Filing: iNymbus automates the process of filing disputes by providing detailed descriptions and attachments. This feature is especially helpful when dealing with major retailers like Amazon, Walmart, and Target, where dispute resolution is often complex. Additionally, it supports email-based submissions for smaller retailers like Nordstrom and Ulta.
-
Improved Speed: The platform dramatically accelerates the dispute resolution process, claiming to be up to 30 times faster than traditional manual methods. This means disputes can be resolved promptly, reducing the time chargebacks remain unresolved.
-
Comprehensive Retailer Support: iNymbus offers support for over 40 retailers, ensuring that compliance with trading partner requirements is fully met. It manages a wide range of deduction claims, including those with special requirements unique to certain retailers.







.jpg)
