In retail supply chains, few documents are more critical and more frequently overlooked than the vendor routing guide. This document outlines how suppliers should ship goods to a retailer’s distribution centers, detailing everything from packaging specifications to carrier selection.
It is not just a guideline. It is a contractual framework that, if ignored, leads to costly chargebacks, delayed payments, and strained partnerships.
This guide breaks down the key elements of vendor routing guides, explains why adherence is non-negotiable, and outlines common violations that trigger deductions.
Key Takeaways
-
✓
Vendor routing guides serve as the operational blueprint for compliant shipping, labeling, and packaging.
-
✓
Ignoring routing requirements leads to chargebacks, delays, and strained retailer relationships.
-
✓
Each retailer publishes its own guide with unique rules and frequent updates that vendors must monitor.
-
✓
Automation tools help vendors validate labels, dimensions, and ASNs to avoid deductions before they occur.
-
✓
Familiarity with common routing violations allows teams to fix upstream errors and reduce revenue loss.
What is a Vendor Routing Guide?
A Vendor Routing Guide is a set of logistics, labeling, packaging, and shipping instructions provided by a retailer to its suppliers. It outlines how goods must be prepared and delivered to meet retailer-specific requirements. Each guide varies by retailer, product type, and distribution strategy, but non-compliance often leads to deductions or chargebacks against the invoice.
A typical routing guide includes:
- Approved carriers and booking windows
- Labeling specifications (UPC, SSCC-18, ASN)
- Pallet configuration and packaging standards
- Delivery appointment procedures
- ASN (Advance Shipment Notice) submission formats
- Routing request portals and lead times
Why Routing Guide Compliance Matters
While the routing guide may seem like a logistics document, it’s also a compliance checkpoint with direct financial consequences. Non-adherence leads to operational disruptions, lost inventory visibility, and automated deductions issued through retailer systems.
Retailers operate on slim margins and tight schedules, so compliance ensures:
- Goods flow predictably into their distribution centers
- Errors don’t ripple downstream to stores or customers
- Reverse logistics and restocking costs are minimized
Failure to follow routing instructions is one of the top reasons for chargebacks in retail.
Common Routing Violations That Trigger Deductions
Routing guide violations come in many forms: some logistical, others technical. Here's a breakdown of typical non-compliance scenarios that generate chargebacks:
| Violation Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Late delivery | Missed delivery windows or appointments |
| Unapproved carrier used | Not following the assigned carrier or route booking process |
| Incorrect labeling | Wrong or missing SSCC–18, carton labels, or ASN details |
| Improper packaging | Non-compliant palletization or damaged packaging |
| Incomplete ASN or EDI errors | ASN was not sent on time or with incorrect data |
| Missing BOL or documentation | Failure to include required shipping documentation |
Real-world Examples of Routing Guide Deductions
Here are some examples of deduction codes used by major retailers:
Walmart:
- Code 22: Merchandise Billed Not Shipped – Occurs when the quantity billed exceeds the quantity received.
- Code 24: Carton Shortage/Freight Bill Signed Short – Applied when fewer cartons are received than listed on the freight bill.
- Code 64: Early Shipment – Issued when goods are delivered before the scheduled delivery window.
- Code 65: Late Shipment – Triggered when deliveries arrive after the agreed-upon delivery window.
Target:
- A030: Carton Shortage – Deduction for discrepancies between invoiced and received carton quantities.
- A032: Damage/Defective – Applied when products are received damaged or defective.
- A036: Cost Difference – Occurs when there is a mismatch between the invoiced cost and the purchase order.
Kohl’s:
- ASN08 – Incorrect vendor ship date in ASN
- ASN11 – Wrong DC or store listed on ASN
- TMS05-09 - Routing accuracy, cancellations, location updates, hazmat flags
- TR003-TR054 - Includes issues like consolidation problems, carrier selection, routing requests, and weight/cube discrepancies.
How to Reduce Chargebacks Caused by Routing Errors
Avoiding these costly issues starts with taking routing compliance seriously. Here's how vendors can get ahead:
1. Centralized routing guide documentation
Maintain a single source of truth for routing instructions, updated per retailer. Routing guides are frequently revised, and relying on outdated SOPs is a fast track to chargebacks.
2. Use a compliance checklist per shipment
Build pre-shipment workflows that check for:
- Carrier confirmation
- Label printing verification
- ASN validation
- Shipment documentation matching
3. Train warehouse and logistics teams
Chargebacks are often preventable at the operational level. Provide training for teams that handle packaging, labeling, and EDI processing.
4. Monitor EDI performance
Routing-related deductions often stem from ASN errors or delays. Monitoring your EDI pipeline for failed transactions can prevent silent violations.
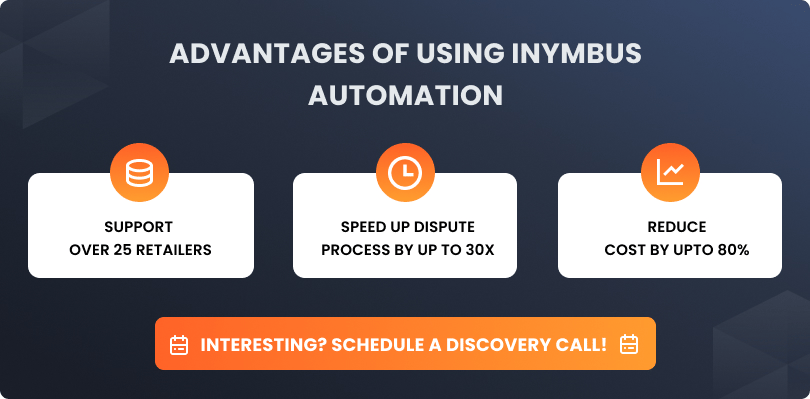
Automate Deduction Resolution for Routing Issues with iNymbus
Even the most meticulous vendors can’t escape every chargeback. But what you can control is how quickly and efficiently you respond.
That’s where iNymbus comes in.
iNymbus automates deduction identification, documentation collection, and dispute submission for routing violations and other common chargeback categories. With pre-built integrations across major retailer portals and EDI platforms, it helps AR teams:
- Identify recurring routing guide violations
- Auto-generate dispute packages with proof of compliance
- Monitor dispute status and recover lost revenue faster
Instead of manually chasing hundreds of invalid deductions, let iNymbus reduce your backlog and increase recovery rates, especially for chargebacks related to ASN issues, shipping errors, and labeling mismatches.
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the difference between a routing guide and a compliance manual?
A routing guide focuses on shipping, labeling, and transportation procedures. A compliance manual may include broader vendor requirements, including pricing, packaging, or returns.
Can I recover money from routing violations?
Yes, if the deduction was made in error or if you have documentation showing compliance. Retailers like Walmart and CVS have formal dispute processes.
Are routing guides standardized across retailers?
No. Each retailer has its own guide with unique codes, shipment procedures, and documentation formats. Always follow the most recent version.
How often are routing guides updated?
Some retailers update them quarterly or annually. Always subscribe to vendor communication alerts to avoid missing revisions.