Amazon Vendor Returns work much like the reverse side of the supply chain. Instead of goods flowing from vendors to Amazon, they move back from Amazon to vendors.
These returns can happen for different reasons, including defects, overstock, or damage, and are always governed by the vendor agreement.
Just as outbound shipments follow a set process from purchase order to delivery, vendor returns follow a structured path from notification to reconciliation.
In this guide, we’ll outline how Amazon Vendor Returns work, the key steps involved, and what vendors can do to manage them more effectively.
What Is Vendor Returns At Amazon?
Vendor Returns at Amazon refer to products that Amazon sends back to its vendors under specific conditions outlined in the vendor agreement. These returns may occur due to product defects, overstock, damages, or other contractual reasons. Unlike customer returns, vendor returns operate within a structured B2B process between Amazon and the vendor.
Key steps in the vendor return process include:
- Identification of Returns: Amazon first identifies products that need to be returned.
- Notification to Vendor: Vendors are then notified with details of the return request, including the reason and supporting documentation.
- Vendor Review: The vendor reviews the request and evaluates it based on agreements and product condition.
- Response: Depending on the review, the vendor may accept the return or dispute it.
- Dispute Resolution: If disputed, Amazon investigates and works with the vendor to reach a resolution.
The complete process is discussed further in the article.
Customer Returns vs. Vendor Returns on Amazon
- Customer Returns: End customers return products they purchased for reasons like dissatisfaction, incorrect fit, or defects. These are handled by Amazon’s customer service and are focused on buyer satisfaction.
- Vendor Returns: Amazon returns goods back to the vendor due to overstock, damage, or quality concerns. The process is governed by the vendor agreement and focuses on supply chain management.
Vendor Returns vs. Seller Returns on Amazon
Even though both vendors and sellers manage return shipping on Amazon, their processes are quite different.
- Vendors Returns: Apply to vendors (manufacturers, brands, or distributors) who sell products directly to Amazon. Returns are more complex, involving bulk quantities and formal agreements.
- Sellers Returns: Apply to third-party sellers on Amazon Marketplace. They manage returns themselves but must follow Amazon’s policies for customer satisfaction.
Reasons Behind Amazon Vendor Returns
These challenges highlight the importance of effective Amazon Returns Management to reduce costs and streamline operations.

Overview Types of Vendor Returns
Here are some reasons why Amazon might return an item to a vendor:
- Poor Sales: Products are returned due to poor sales performance or because they are outdated.
- Expired Items: Products that have passed their expiration date while stored in Amazon's warehouse. These items cannot be sold and are returned to the vendor for proper disposal or other actions.
- Damaged Products: Items damaged at any stage, be it warehouse or be it during transit, are returned to maintain retailer standards.
- Canceled Orders: Whenever there is a change in demand for the product it is possible for the retailer to cancel the order. This would result in a return if it was already dispatched.
- Regulatory Compliance: Retailers have regulatory compliance and when vendors fail to meet them, there is a possibility that the retailer might return the goods of that vendor.
- Overstock: Products that are in excess at Amazon’s warehouse and do not have a great demand. Such items are returned to the vendor to free up space and reduce storage costs.
- Defective: Products that have functional issues or defects that make them unusable or unsellable. These items are typically returned by customers due to quality issues or failures.

Amazon Returns Management: The Vendor Process Explained
The Return To Vendor (RTV) process refers to the procedure of returning products, materials, or merchandise to the original supplier or vendor from whom they were purchased. Amazon vendor returns process includes the steps below:
- Identification of Returns: The Amazon return processing starts with Amazon identifying products that need to be returned to the vendor. This could be due to various reasons such as explained above.
- Notification to Vendor: Once a return is identified, Amazon notifies the vendor about the return request. This notification includes details about the product, the reason for return, additional information, and any relevant documentation.
- Vendor Review: Once the notification is received, the vendor reviews the details of the return request. They assess the reason for the return and determine whether to accept or reject the return.
- Response: The response is based on the vendor's policies, contractual agreements with Amazon, and the condition of the returned item. Depending on the assessment, the vendor either accepts returned merchandise or disputes the return.
- Dispute Resolution: If the vendor disputes the return, Amazon reviews the dispute and works towards resolving the issue. This could involve further investigation, communication between the parties involved, and reaching a resolution.
For more info check out our webinar on Amazon Return Processing.
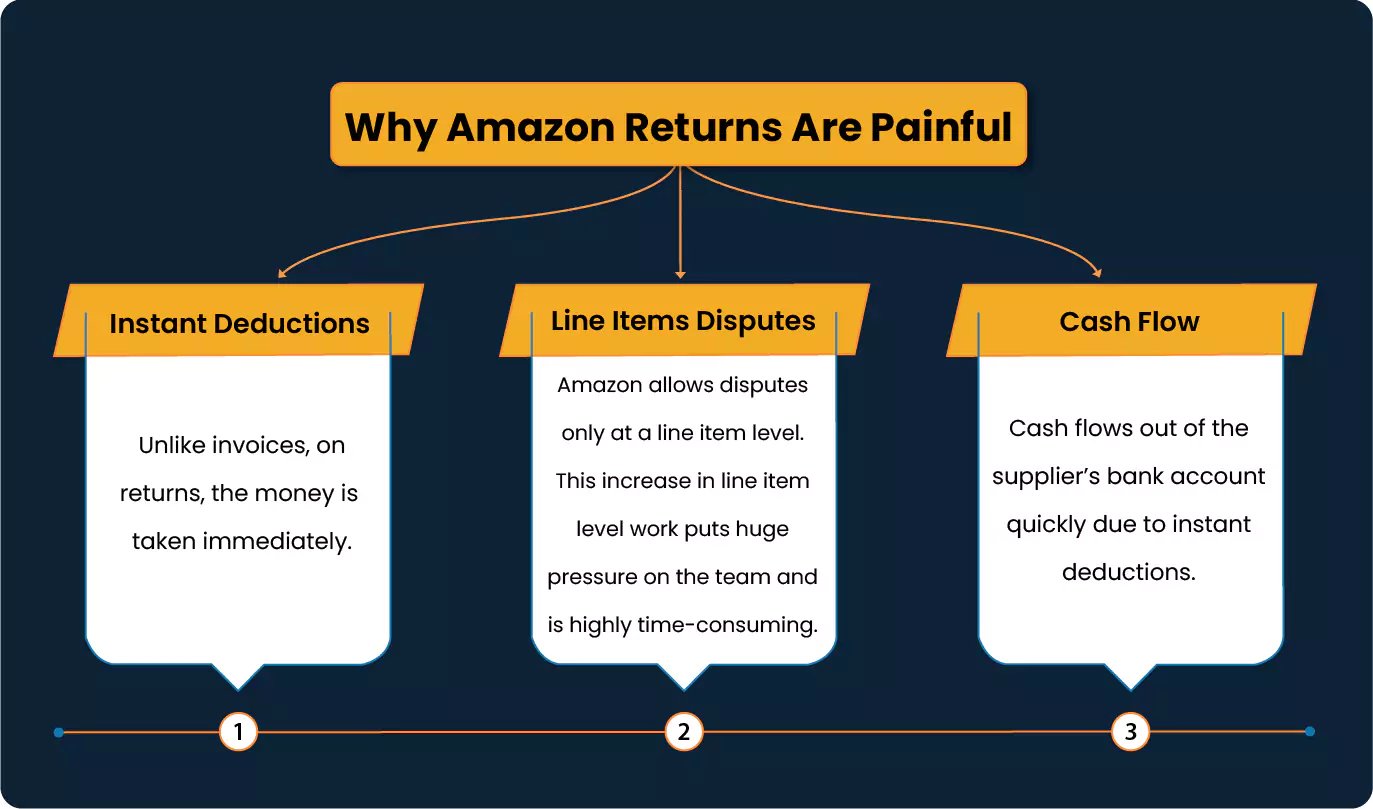
Why Amazon Returns Are Painful
Poorly managed returns processes make Amazon Returns Management challenging for vendors, leading to inefficiencies and higher costs.
Challenges In Returns Management For A Large Distributor
- Lengthy Return Process: Returns take a long time to process, tying up resources.
- Technological Disadvantages: Retailers such as Amazon have advanced technology for managing returns, placing suppliers at a disadvantage.
- Soaring Return Rates: Increasing return rates add to the complexity and cost of return management.
- Limited Progress: No significant results in progress are achieved even after putting in continuous efforts.
- Communication Overload: Managing returns involves a high volume of communication between various parties, leading to potential errors and inefficiencies.
Best Practices for Amazon Returns Management
- Use technology to automate repetitive processes.
- Analyze return trends to reduce defective or low-demand inventory.
- Optimize communication between vendors and Amazon.
- Implement an efficient dispute resolution system with tools like iNymbus.
iNymbus for Amazon Returns Processing
With the help of Robotic Process Automation (RPA), iNymbus improves the efficiency and reliability of returns management for distributors. iNymbus can automate data entry, handle reconciliations, and upload disputes to Amazon’s portal line-by-line. This automation significantly reduces human errors, increases processing speed, and improves overall efficiency.
Benefits of iNymbus
- Reduced Labor Costs: Businesses can significantly reduce the cost by automating labor-intensive tasks associated with returns management.
- Automated System: Our system reduces errors and saves time spent on corrections.
- Adaptable to Volume: Easily scale operations up or down based on return volumes, especially during peak seasons.
- Data Integration: Our system integrates data from ERP systems, checks its accuracy, and reconciles information from web portals for reliable returns processing.
- Focus on Strategic Tasks: Employees can focus on higher-value tasks such as analyzing return patterns and identifying root causes.

For more information on Amazon Chargebacks, do check our whitepapers on Amazon Vendor Returns and Recovery Percentages.